
EMS Calibration
Vehicle
Calibration

Target vehicle
- Gasoline
- Diesel
- Hybrid
- EV
Calibration
- Emission
- OBD-II
- Driveability
- After treatment system
Emission calibration
- SULEV, EURO 6 / 7, China 6 and Tier 4 (Industrial)
- Emission related hardware and component selection
- Optimization of logic and calibration for leaner cold fueling
- UREA-SCR application
- DPF calibration

Drivability calibration
- Optimum calibration for high drivability index fuel
- Logic development for high drivability index fuel
- Drivability calibration over -30 ˜ 50。... ambient temperature
OBD-II calibration
- OBD-II, EOBD and KOBD regulation
Vehicle benchmarking
- Emission related hardware, logic and calibration
- Fuel economy related hardware, logic and calibration
- Drivability related logic and calibration
Fuel economy analysis
- Energy Flow-Down Method
Development of advanced fuel economy system and logic
Catalyst bench aging and vehicle durability cycle development corelated with in-use DF
Gasoline
SULEV application
Fast light-off control
-
H / W side
- Place the catalyst as close as possible to exhaust manifold
- Increase catalyst cell density
-
Calibration side to increase heat flux
- Increase Idle engine speed
- Spark timing calibration
- Waste-gate position open control
Reduce engine-out raw emissions
: optimum catalyst heating point and cold start
- Intake / exhaust VVT control
-
Injection strategy calibration
: SOI, EOI, fuel pressure, split injection calibration
NOx conversion efficiency increase
- Fuel cut off condition calibration
- Catalyst purge calibration to increase NOx conversion efficiency
- Lambda control calibration with downstream O2 sensor feedback
Gasoline
particulate
filter control
GPF model calibration
- DP soot mass with clean filter model
- Engine out soot model
- Soot burning rate model
- GPF temperature model
GPF control
-
Passive / active regeneration control
(Lambda, temperature control) - Fuel cut off conditon calibration during regeneration
- Soot mass validation (model vs actual mass)
- Soot burning efficiency test
- Service regeneration strategy
- GPF regeneration strategy (duration, coordinator)
- GPF OBD (efficiency) strategy
GPF validation test
-
GPF failure check through uncontrolled burning test (DTI, DTO)
: CT scanning confirmed - Environment test (cold, hot, altitude)
- Ash calibration with fleet test
Diesel SCR control
SCR model calibration
- Raw NOx, NO / NO2 ratio modeling
- NOx conversion efficiency modeling
- NH3 loading / slip modeling
- SCR temperature model
- SCR efficiency model
SCR Control
- Heat-up
- NH3 loading target
- Urea dosing schedule
- SCR defrost calibration in cold condition
- Strategy for improvement of emission(RDE, WLTC, NEDC, etc.)
- SCR OBD strategy(efficiency, incorrect urea, consumption, etc.)
SCR validation test
- Environment test(cold, hot, altitude)
- Validation of model accuracy
- Robustness of NOx conversion efficiency in real driving
Diesel
particulate
filter control
DPF model calibration
- DP soot mass with clean filter model
- Engine out soot model
- Soot burning rate model
- DPF temperature model
DPF control
- Heat-up / active regeneration control (air control, post injection control)
- Open & closed loop temperature control
- Transient conditon check and calibration
- Soot mass validation (model vs actual mass)
- Soot burning efficiency test
- Service regeneration strategy
- DPF regeneration strategy (duration, coordinator)
- DPF OBD (PM sensor, efficiency) strategy
DPF validation test
-
DPF failure check through uncontrolled burning test (DTI, DTO)
: CT scanning confirmed - Environment test (cold, hot, altitude)
- Oil dilution & ash check with fleet test
Diesel
EURO 7 / China 6
Additional challenge for better fuel consumption
-
Thermal management
- Integrated thermal management 3-way valve control(block, radiator, heater)
- Split cooling circuit
- Optimized temperature of each part
-
Weight reduction
- Aluminum cylinder block
-
Friction reduction
- Piston & ring design optimization
- Crankshaft balance weight optimization
- Variable oil pump integrated with vacuum pump
- Timing belt instead of chain system
- Camcarrier-camshaft module
- Crank offset
- Roller rocker arm
- Switchable water pump or electrically controlled thermostat
After treatment system
- SCR system will be in multiple locations and the total size will be larger
- Urea injection will be multi-point injection.
- DPF would not need active regeneration any more, only passive type would be enough.
- Electrically heated catalyst could be used for cold start emission.
Combustion system
- With enhanced SCR system, engine developmint could be focused only on better thermal efficiency and on reducing PM, no longer on reducing NOx emission as before.
- Compression ratio would be raised to around 18 from current 15~16.
- EGR would be used limitedly or the system even may be deleted.
- High swirl would be required less than before, therefore port could be optimized for more flow.
Electrification
- 48V mild hybrid system will used.(P0~P2)
- EHC could be effective by 48V system
Fuel Economy
Analysis
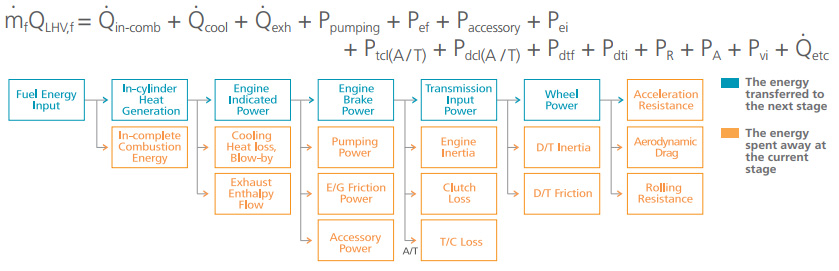
Principle of Energy Flow-Down Method
To improve fuel economy of your car, understanding of engine + T / M + vehicle interaction and control strategy (ECU, TCU) are very Important
Benets of Energy Flow-Down Method
- Energy Flow-Down Method can analyze the fuel consumption and contribution of each component and ECU / TCU control data through systematic approach.
- Client can have the whole view for the quantitative fuel consumption and contribution of each component.
- Client can recognize the weak and strong points against target vehicle.
- Client can understand how top maker optimizes every component and control data to improve fuel economy.
- Client can make catch-up plan of short, mid, long term in the most efcient cost.
How we do,
What you can get!
Measurement items
- Combustion pressure
- Ignition signal
- Engine speed
- Vehicle speed
- Manifold absolute pressure
- Air / Fuel ratio
- Battery voltage & current
- Alternator current
- Cooling fan current
- Brake pedal signal
- Accelerator pedal signal
- Throttle angle signal
- Coolant temperature
- Engine oil temperature
- Injection pulse
- Fuel rail pressure
- Fuel temperature
- Exhaust gas temperature
- Turbine rpm
- Output shaft rpm
- Engine inertia @ lift
- Drivetrain friction @ lift
- Drivetrain inertia @ lift
- Engine friction @ bench
-
Torque converter
characteristics @ MAD - Injector characteristics @ rig
- Power steering friction @ rig
-
Each gear driving resistance
@ test load (if necessary) - Shift pattern & lockup area @ MAD
Results
- Indicated thermal efficiency
- Incomplete combustion loss
- Pumping loss
- Engine friction loss
- Alternator loss
- Power steering loss
- Engine inertia loss
- Torque converter base loss
- Torque converter slip loss
- Braking loss
- Drive train friction loss
- Drive train inertia loss
- Clutch loss
- Vehicle inertia loss
- Rolling resistance loss (f0)
- Aerodynamic resistance loss (f2)
- Pilot / Main injection timing (diesel)
- Spark timing (gasoline)
- Idle RPM
- Total fuel cut time
- Total cycle number
- Cooling fan loss
- Total part load full lockup time
- Part load speed ratio distribution
- Total driving time at each gear
- Shift pattern
- Energy management system logic
- Neutral control logic
- Deceleration lockup logic
- Ne elevation logic
Recommendation
- Logic & calibration strategy
-
Engine hardware strategy
- Friction improvement
-
System application strategy
(Intake CVVT, Dual CVVT, Turbo, GDI, etc.)
-
Characteristic of engine
(BSFC, mechanical friction, pumping friction, engine inertia) - Transmission hardware strategy
- Shift pattern & lockup zone strategy
- Torque converter selection strategy
- Gear ratio selection strategy
-
Transmission related loss
(Drivetrain friction loss, slip loss, fuel consumption at each gear) - Vehicle thermal management strategy
- Vehicel electrical load strategy
- Vehicle energy save strategy
- Rolling resistance reduction strategy
- Aerodynamic resistance reduction strategy